Commands Search App
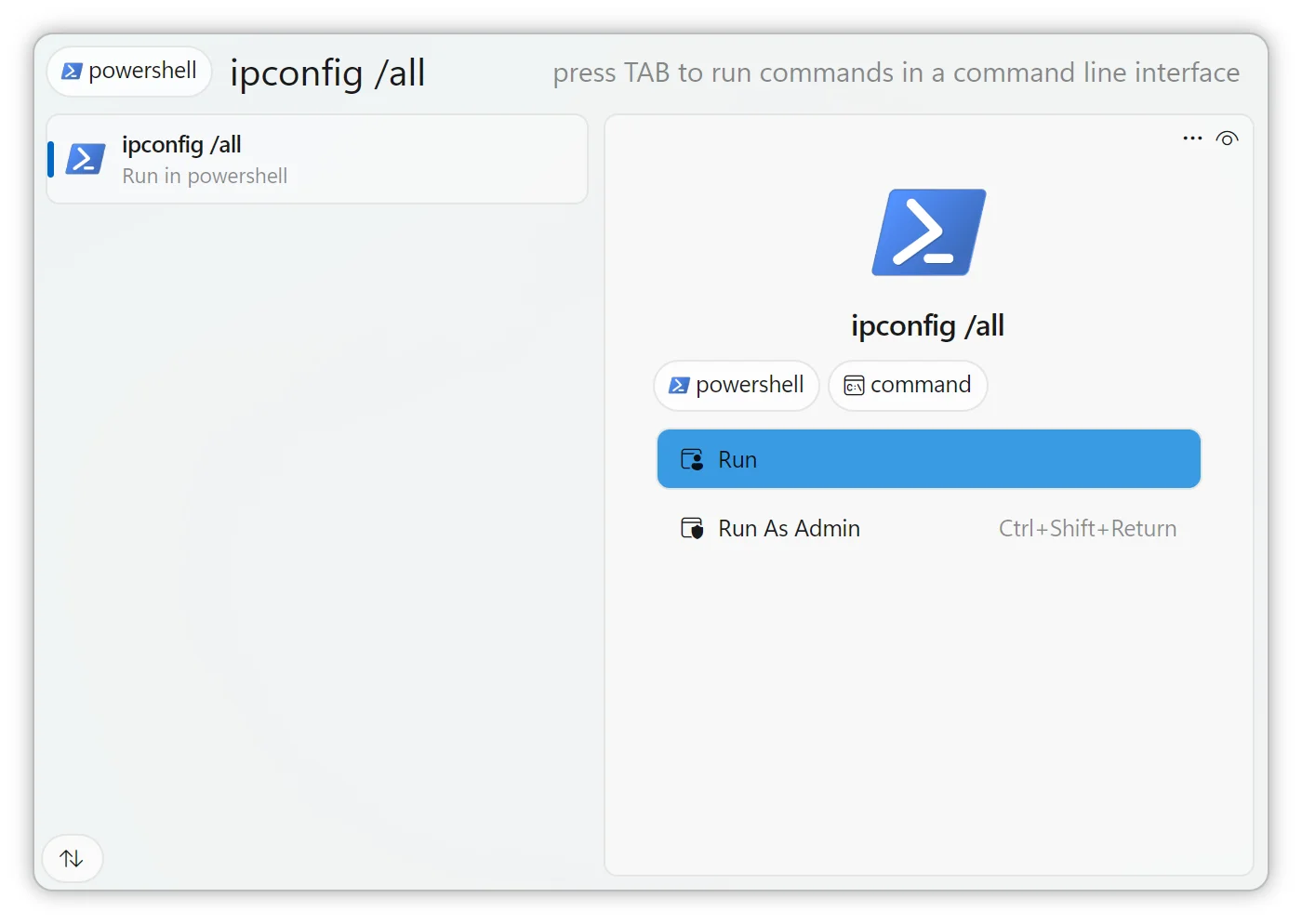
The Commands Search App lets you execute command-line instructions, system operations, and previously run commands directly from Fluent Search. No need to open a terminal window first — run commands as fast as you launch an app.
What it does
- Run shell commands through your configured command-line interfaces (PowerShell, Cmd, Git Bash, WSL, etc.)
- Execute system operations like shutdown, restart, sleep, lock, and media controls
- Access command history to quickly re-run previously executed commands
- Windows Run emulation to open paths, run executables, and expand environment variables
Search Tags
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
command |
General command search |
Run |
Emulates the Windows Run dialog — run an executable, open a path, or expand environment variables |
Powershell |
Run a command directly in PowerShell |
Cmd |
Run a command directly in Command Prompt |
| (custom CLIs) | Any additional command-line interfaces you configure |
To use: Type the tag name → press Tab → type your command.
Examples:
Run+Tab→notepad.exePowershell+Tab→Get-ProcessRun+Tab→%windir%\System32
System operations
When Search for system commands is enabled (on by default), Fluent Search can run OS-level operations:
| Category | Operations |
|---|---|
| Power | Shutdown, Restart, Sleep, Hibernate, Lock |
| Media | Play/Pause, Next track, Previous track, Volume controls |
| Display | Screen off |
System operations appear as results when you search for related terms (like typing "shutdown" or "restart"). Some operation groups can be expanded to show sub-operations.
Command history
Fluent Search automatically tracks commands you run and makes them searchable:
- Start typing keywords from a previously run command to see it in results
- Select a command from history and press
Enterto re-run it - PowerShell history from PSReadLine is also imported, so commands you ran in external PowerShell sessions appear too
Result actions
| Action | Shortcut | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Run | Enter |
Executes the command |
| Run As Administrator | Ctrl + Shift + Enter |
Runs the command with elevated privileges |
Configuring command-line interfaces
You can add multiple CLIs so Fluent Search works with your preferred shell environments:
- Go to Settings → Apps → Commands → Command-Line Interfaces
- Click Add and provide:
- Name — A descriptive label (for example, "Git Bash", "WSL Ubuntu")
- Executable Path — Full path to the CLI executable
- Arguments — Default arguments. Use
%sas a placeholder where the search text should be inserted
Common CLI configurations:
| CLI | Executable | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| PowerShell | powershell.exe |
Default on most Windows systems |
| Command Prompt | cmd.exe |
Classic Windows shell |
| Windows Terminal | wt.exe |
Modern terminal host |
| Git Bash | C:\Program Files\Git\bin\bash.exe |
Git for Windows |
| WSL | wsl.exe |
Windows Subsystem for Linux |
Setting a favorite CLI
You can designate one CLI as your favorite. The favorite CLI is used by other Search Apps for related operations — for example, when you open a file's parent folder in the command line from the Files Search App.
To set a favorite:
- Go to Settings → Apps → Commands → Command-Line Interfaces
- Click the star icon next to your preferred CLI
Settings
| Setting | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Search in Run | Execute commands using the Windows Run mechanism | On |
| Search for system commands | Include system operations (shutdown, restart, media controls) in results | On |
| Command Line Interfaces | Configure available CLIs with name, path, and arguments | PowerShell, Cmd |
To access: Settings → Apps → Commands.
Tips
- The
Runtag is incredibly versatile — use it to open any path, run any executable, or type environment variable paths like%appdata%or%temp% - Use
Ctrl + Shift + Enterwhen a command needs administrator privileges - If you frequently run the same set of commands, consider creating a Task to automate them
- Set up your favorite CLI so that "Open in Command Line" from the Files Search App opens your preferred shell